
Atom diagram Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
Oxygen, atomic. Molecular Formula O. Average mass 15.999 Da. Monoisotopic mass 15.994915 Da. ChemSpider ID 140526.
Atomic Model Of Oxygen ClipArt Best
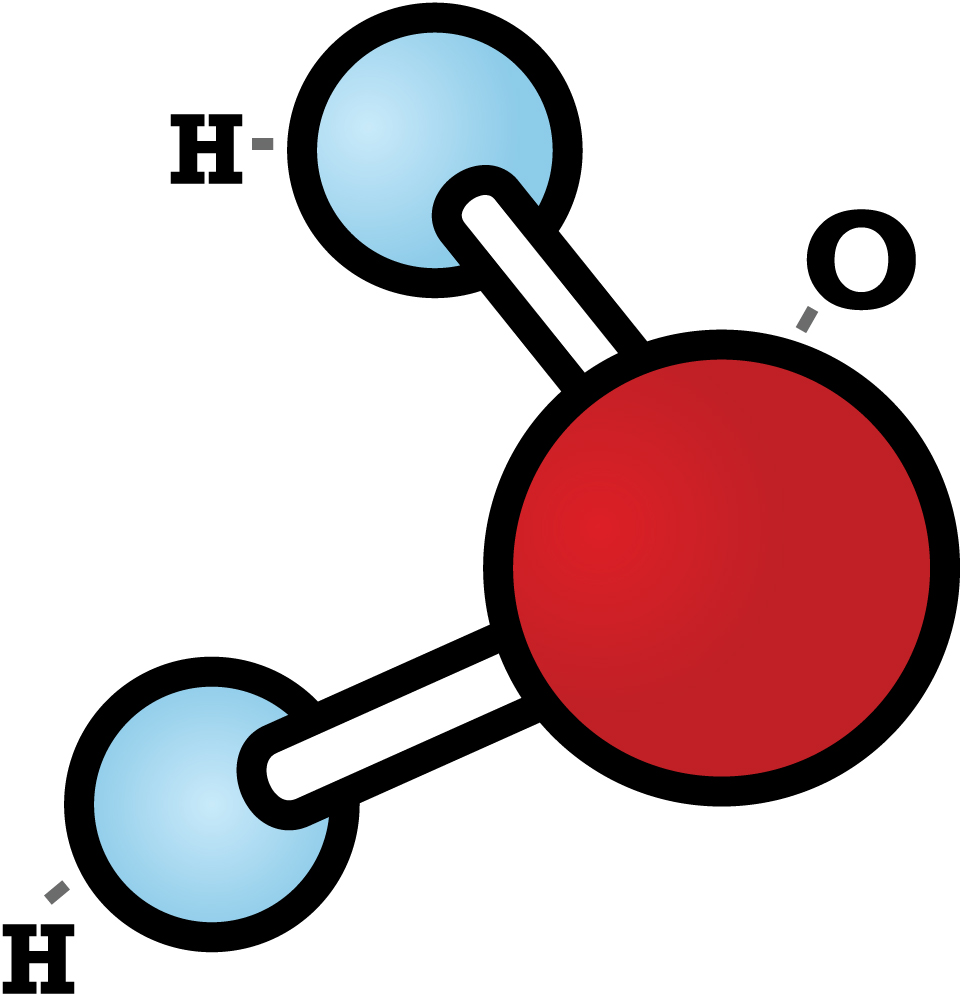
Oxygen is a chemical element - a substance that contains only one type of atom. Its official chemical symbol is O, and its atomic number is 8, which means that an oxygen atom has eight protons in its nucleus. Oxygen is a gas at room temperature and has no colour, smell or taste. Oxygen is found naturally as a molecule. Two oxygen atoms strongly bind together with a covalent double bond to.

Oxygen, atomic structure Stock Image C013/1508 Science Photo Library
The Naked Scientists Periodic Table of Videos Created by video journalist Brady Haran working with chemists at The University of Nottingham. Element Oxygen (O), Group 16, Atomic Number 8, p-block, Mass 15.999. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.
Oxygen Atom On White Background Stock Illustration Illustration of scheme, blue 51926655
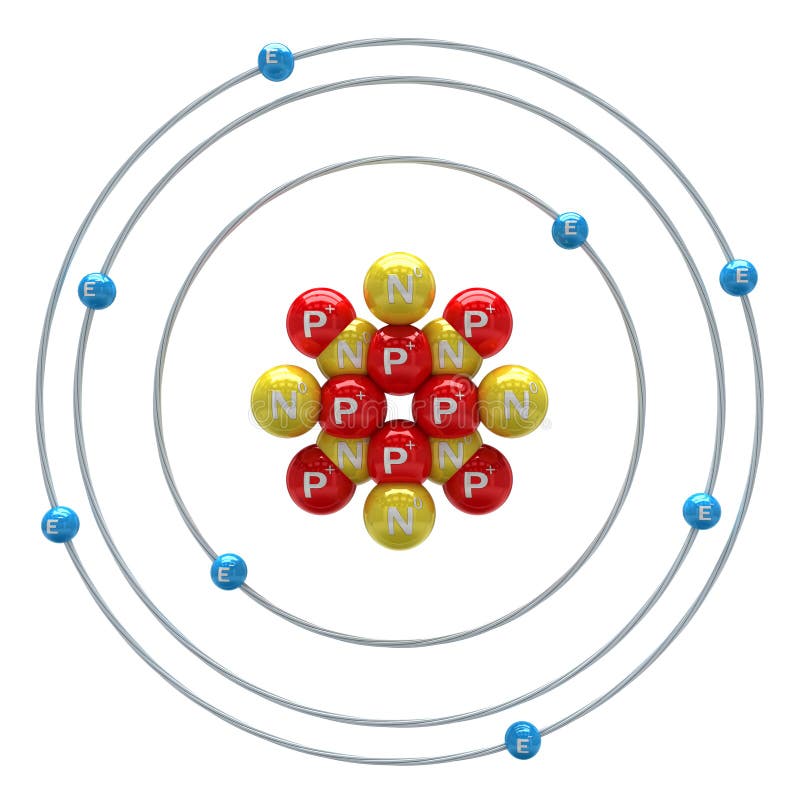
Atomic Number of Oxygen. Oxygen is a chemical element with atomic number 8 which means there are 8 protons and 8 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Oxygen is O. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons.

Diagram representation of the element oxygen Vector Image
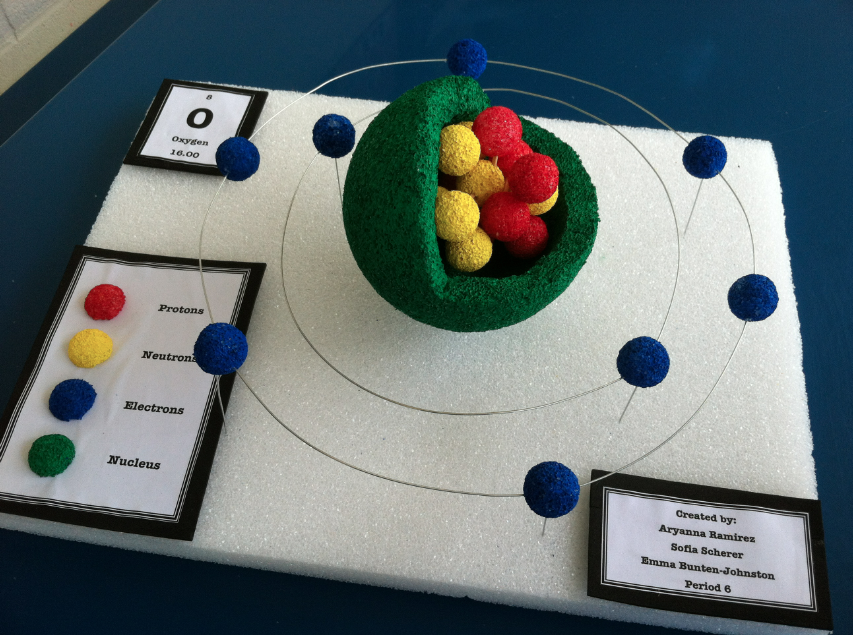
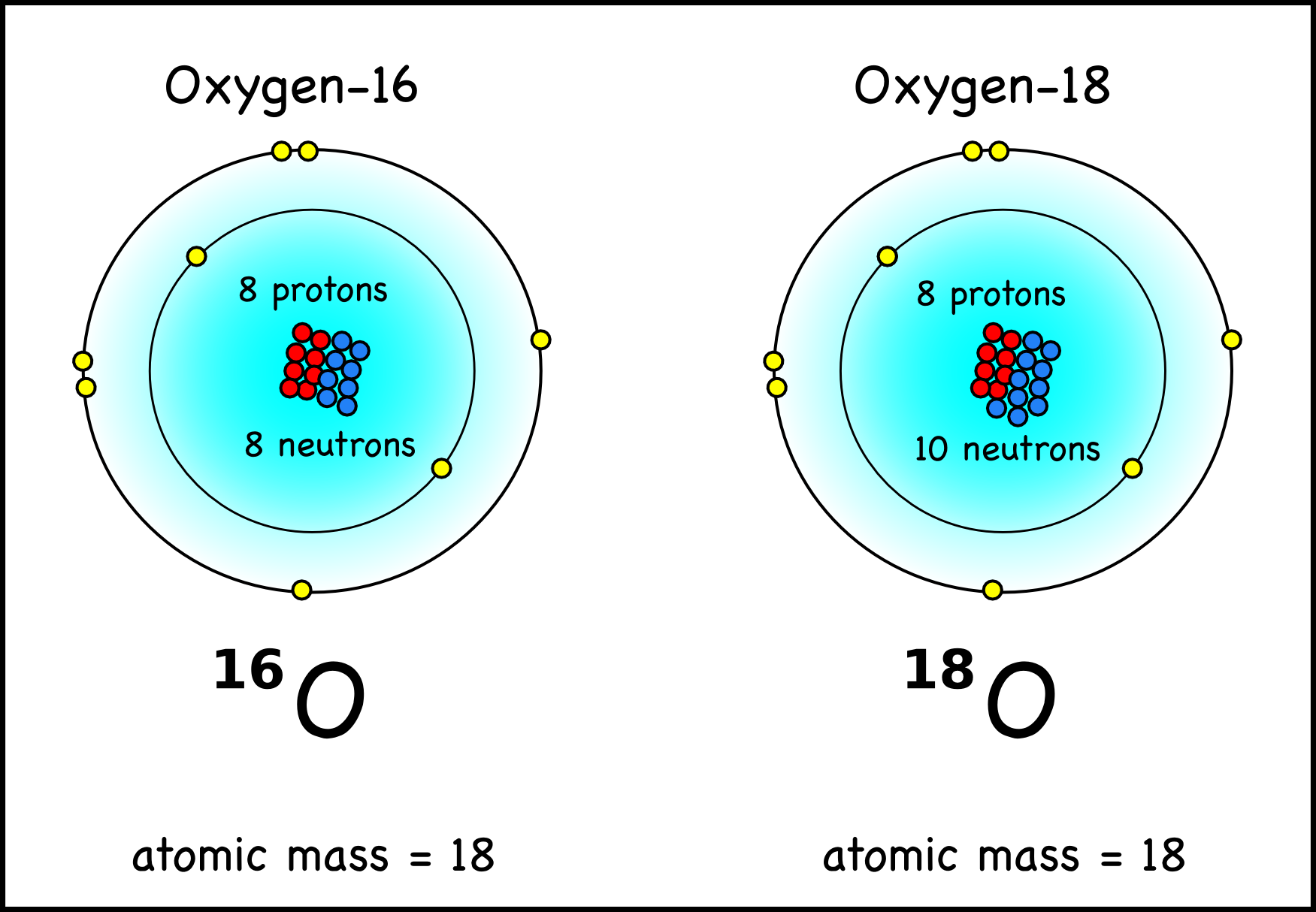
Atomic structure . Atomic structure signifies the structure of an atom encompassing a nucleus in which the protons are positively charged and neutrons that are neutral are present.The negatively charged particles are called electrons which spin around the center of the nucleus.; The addition of the total number of protons and neutrons existing in the nucleus of an atom is known as the mass.

Oxygen atomic structure, artwork Stock Image C016/4341 Science Photo Library
Characteristics and Molecular Structure of Oxygen. Oxygen is a chemical compound with symbol O and atomic number 8. In the periodic table, it is the member of the chalcogen group, an extremely reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily produces oxides with most elements as well as with other elements.
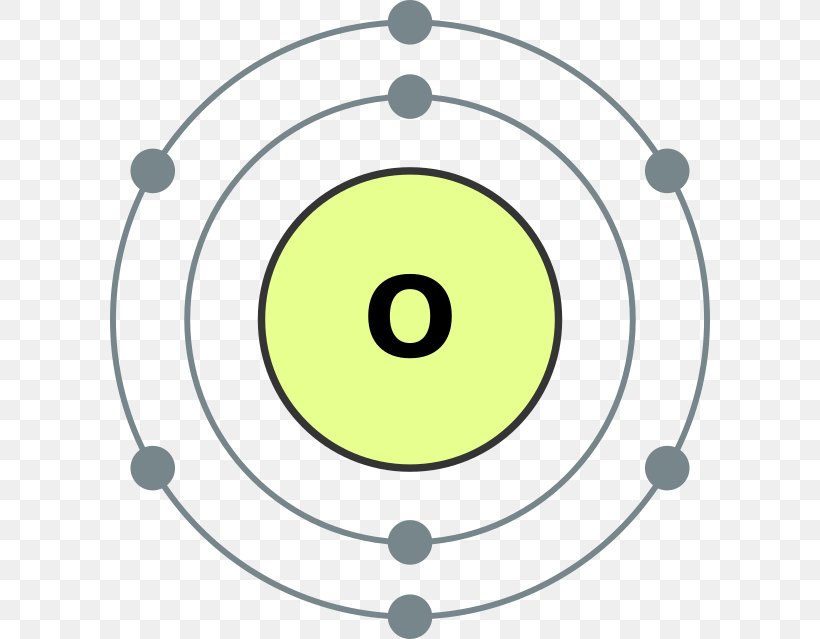
Bohr Model Atomic Number Oxygen Diagram, PNG, 600x639px, Bohr Model, Area, Atom, Atomic Number
In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Oxygen atom (O). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons a.

FileElectron shell 008 Oxygen.svg Wikimedia Commons Atom diagram, Electron configuration
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in Earth's crust, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe.

Why does oxygen form the "O"_2^(2) ion? Socratic
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
paleontology Montessori Muddle
Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.

Oxygen, atomic structure Stock Image C045/6426 Science Photo Library
Atomic structure - AQA Structure of the atom. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be.

Oxygen atomic structure, artwork Stock Image C016/4342 Science Photo Library
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in Earth's crust, and after hydrogen and helium, it.
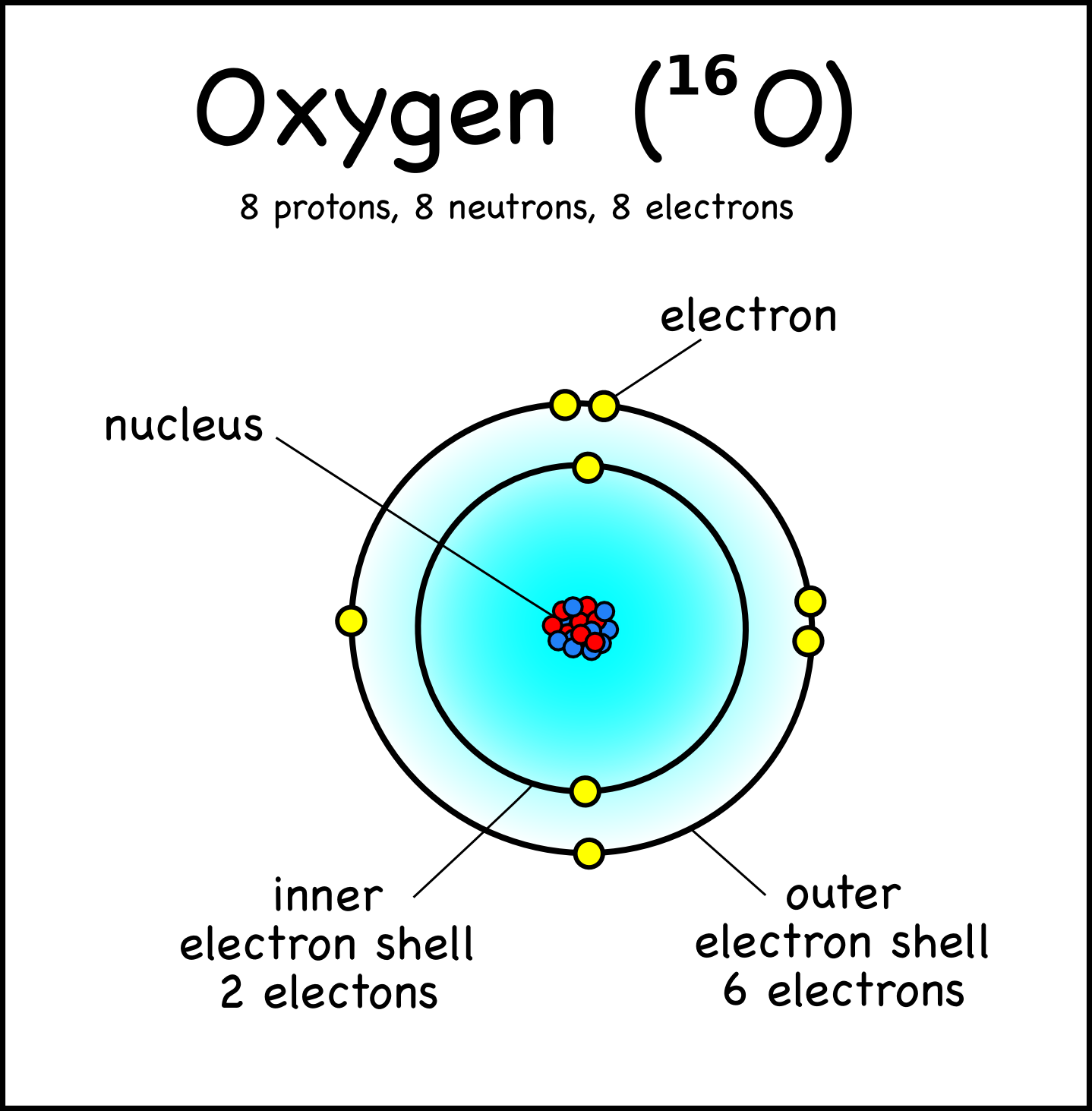
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle
Oxygen is a chemical element. It has the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is the third most common element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium. Oxygen is more than a fifth of the Earth's atmosphere by volume. In the air, two oxygen atoms usually join to make dioxygen (O 2), a colourless gas. This gas is often just called oxygen.

Oxygen Valence Electrons (O) Oxygen Valency & Electron Configuration
Magnetic Properties of Oxygen. Oxygen (O 2) is paramagnetic.An oxygen molecule has six valence electrons, so the O 2 molecule has 12 valence electrons with the electron configuration shown below:. As shown, there are two unpaired electrons, which causes O 2 to be paramagnetic. There are also eight valence electrons in the bonding orbitals and four in antibonding orbitals, which makes the bond.
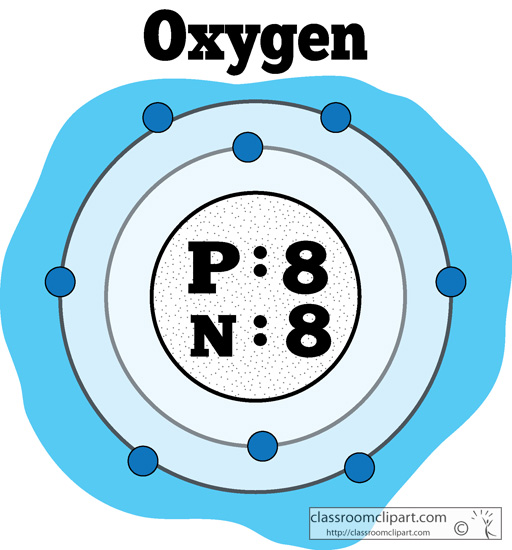
Chemical Elements atomic_structure_of_oxygen_color2 Classroom Clipart
Atomic Structure of Oxygen. Properties of Oxygen. Physical Properties of Oxygen. Oxygen, denoted by the chemical symbol O, is a fundamental element known for its life-sustaining properties. Here are the detailed physical properties of oxygen: Phase: Oxygen is a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP). However, it can be converted into a.
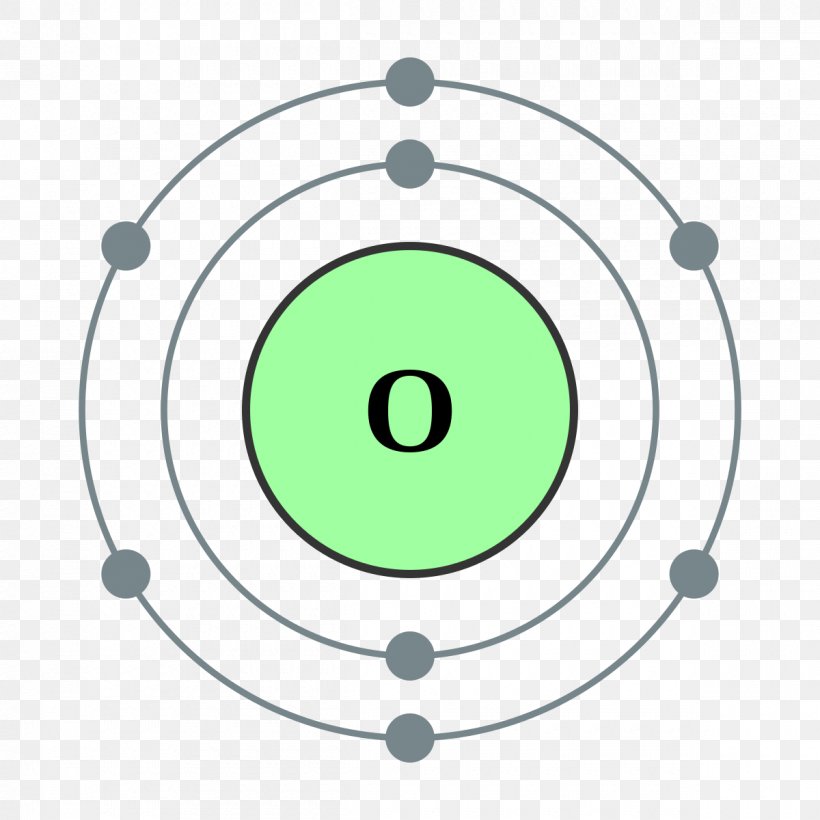
Bohr Model Chemical Element Oxygen Atomic Theory, PNG, 1200x1200px, Bohr Model, Area, Atom
Occurrence and properties. At 46 percent of the mass, oxygen is the most plentiful element in Earth's crust. The proportion of oxygen by volume in the atmosphere is 21 percent and by weight in seawater is 89 percent. In rocks, it is combined with metals and nonmetals in the form of oxides that are acidic (such as those of sulfur, carbon, aluminum, and phosphorus) or basic (such as those of.